Linear Equations
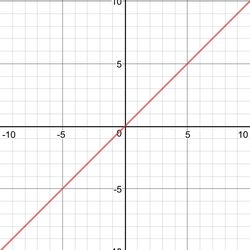
A linear equation is an equation of a straight line.
Usually, this straight line has a set of values, with one being dependent on the other.
Often the independent variable is x, while y is the dependent variable. (meaning that the value of y depends on the value of x)
Even though the values of x and y may change, the values of m and c would not change. (They are referred to as "constants") with m representing the gradient (how steep the line is) and c representing the y-intercept (the y value that the line intercepts the y-axis)
Quadratic Equations
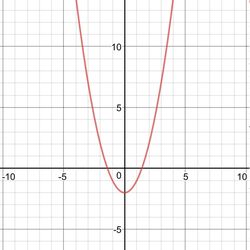
A quadratic equation is equation having the form
y = ax2 + bx + c
x represents an unknown, while a, b, and c represent known numbers where a does not equal to 0.
A projectile line is a common example of a qudratic equation.
Usually, values of the equation would determine the shape of curve as when the values are negative the shape is ⋂(sad face), while when the values are positive the shape is ⋃(smiley face)
Often the variables determining shape are a, b and c which are numerical coefficients.
Cubic Equations
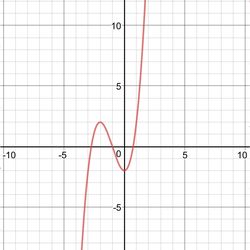
A cubic equation is equation having the form
y = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d
x represents an unknown, while a, b, c and d represent known numbers where a does not equal to 0.
A roller coaster with an up and down is a common example of a cubic equation.
Usually, values of the equation would determine the shape of graph as when the values are negative the shape is an inverted N, while when the values are positive the shape is similar to N.
Often the variables determining shape are a, b, c and d which are numerical coefficients.